simon.jones@leeds-art.ac.uk
Human subject
What it is, what it's used for, two of the key people invovled in psychoanalysis
Sigmund Freud
- development of the psyche from birth
- the development and role of the unconscious in our everyday ives
- the development of gender identity- psycho-sexual identity
- Understanding the complexities of human subjectivity
theory of sexuality, sexual identity
first theoretical which established the psychological concept of
human subjectivity
Not only a form of therapy "the taling cure" a theory of the mind "psyche" and a model-based theory that can be applied to other objects and processes
Our desires, what we are motivated by, etc.
Not just a form of therapy...
- A way of categorising and understanding desire, motivation, dreams .
In it's history has been adopted by artists, designers, architects, public relations, psychotherapists
Establishes that we are not entirelly in control of what we do. Our unconscious plays a part in our day-to-day goings on.
Sigmund Freud
Conceived the idea in the late 1890s
Treated hysteria patients using psychoanalysis by guiding them to discover and accept repressed thoughts/events
Freud asked how can a mental/psychological issue translate into a physical symptom
Dreams: analysed his own and others dreams in terms of their hidden associations and wish-fulfillment
Also observed infants in their habits and associations with parental figures.
OEDIPUS COMPLEX
Oedipus is from Greek mythology. Seduced his mother and killed his father. Freud used this as an analogy/metaphor for something else.
Freud stablished the psychoanalytic theory that allowed or a dynamic unconscious of the mind
THE DYNAMIC UNCONSCIOUS
created through infancy to protect our conscious selves from events, ideas and thoughts that are not acceptable to consciousness
Continues to affect our conscious selves in SOME* ways
The unconscious is chaotic, without order and without language.
Makes itself present through ticks, slips and symptoms (e.g. Freudian slip)
Freuds hysteria patients developed debilitating symptoms as a result of experiences or feelings that had become repressed.
The Freudian slip is generally referred to as something sexual. Not just about that, it is when you accidentally say something. Accidentally slips out, not what you consciously/planned to say. Just sort of happened.
STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT
Our development into willful, conscious beings is full of confusing contradictory and misapprehended thoughts and ideas
An attempt to make sense of both our biological instinctual self and our logical thinking self
We create associations and assumptions through sense data...often incorrectly
The developing child goes through stages: oral, anal and phallic.
Also the child develops preconceptions that must be dealt with in order to develop succesfully - oedipus complex, castration complex, penis envy.
PSYCHO-SEXUAL IDENTITY
The identity we assume by our development in infancy and our body and other peoples bodies
- Oedipus comples - sexual/love feelings towards mother and resentment of father..through childhood dependence and self-centered world view
Oedipux complex - feelings of love, rivaly jealousy all mixed...confusing feelings 'to want' vs 'to be wanted'
Misunderstood.
Not necesarily sexual or incestual ideas of how we know them.
Development of both masculine and feminine identities are in relation to the penis/phallus.
When young infants experience other children, particularly opposite sex. The boy assumes when looking at a girl assumes she's been castrated. Castration complex
Castration complex - the boy fears castration while the girl accepts that she has already been castrated. The phallus as a symbol of power
Penis-envy - at the same time the girl realises she doesn't have a penis. Assumes she's already been castrated. A way to relate to the father-figure
Presence/absence - both create possible negative feelings: the boy fears his castration (powerlessness) while the girl feels that she is missing something.
The child must experience and overcome these issues and mixed feelings in order to become a happy and mentally healthy human subject. In order to gain a sexual identity and a speaking position within the order of language and society
Misconceived and contradictory ideas of gender, power and identity continue to work unconsciously through our lives.
THE UNCANNY
'unhomely'
Something that is simultaneously unnatural yet familiar.
Something that was supposed to remain hidden which has come to the open
Where the boundary between fantasy and the reality break down
Analogies between the unconscious (psychology) and the uncanny (aesthetics)
Some producers of horror films have used the idea of the uncanny. Creating something that has the essence of something familiar, at the same time completely foreign. Creates a sense of unease. Something that should be hidden but has in fact come alive.
The surrealists such as Dali used the uncanny quite a lot to create paintings quite a lot to create stuff kind of ordinary but subversive, surrealised.
Freudian models
Id, ego and superego.
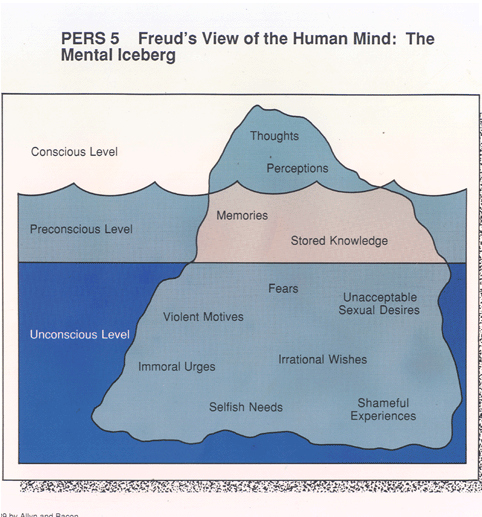
Unconscious, preconscious and conscious.
Iceberg metaphor.
Id, ego an superego.
ID EGO AND SUPER-EGO
Social rules. Politness, customes and traditions
Bio-social-individual beings
Id (unconscious) - represents the biological/instinctual part of ourselves
Ego (conscious) - represents the individual/personality of ourselves
JACQUES LACAN
Frenchman. Comes from tradition of philosophy/
In the 60s and 70s Lacan presented his own brand of psychoanalysis claiming a 'return to Freud'
He reconceptualised Freud's findings through the theoretical model of structural linguistics. Singnification
Lacan posted that the development of the psyhce is entwined within the structures of language...language molds us as much as we mould it.
Subjectivity is paradox
Semiotics
THE MIRROR STAGE
The stage at the point where the child recognise it's own reflection. The reflection of themselves in other peoples, outside himself. Parents etc
Rivalry. The child may recognise it's own image and it is still limited in movement and dexterity
Thus...resulting in the formation of ego which aids and continues to aid a reconciliation of body and image/subjects and other.
Captation. the process by which the child is at once absorbed and repelled by the image of itself (the specular image)
Creating an identity for ourselves. Our behaviour,morals, how we're gonna live. To fulfill this gap of alienation.
Sometimes you might look into the mirroe and think "who am I?" is this how I'm seen to other people?
LACANIAN UNCONSCIOUS
The unconscious is structured like a language
That's not to say that the unconscious has a language but its structure is LIKE a language. Freud said the unconscious is without language? Lacan, said it's LIKE a language.
Connection between unconscious detail and conscious detail.
Highlighting the ways in which meaning in encoded within in linguistic signs - written or spoken words
Unconscious details are encoded in various ways as they slip into consciousness
The big Other and the little other
METAPHOR/METONYMY
Symptom:
- the metaphor - a word is used to represent something else which possess similar characteristics
- Symptoms are translated elemts of unconscious material adopting a metaphor-style coding
Desire:
- Metonymy - a part of something used to represent the whole or the whole used to represent a small part. Meaning is displaced
Referring to your car as your 'wheels' is an example of metonymy
A chain of similar associations
The desire can never be fulfilled, the desire displaced for what cannot be attained...unconscious desire...
LACANIAN PHALLUS
Not the biological penis but a symbol or power/order.
Attained through it's associated LACK - the potential of lack (male) and the actual lack (female)
Masculinity/femininity are not biological definitions but symbolic positions
Our interactions/relations to the symbolic phallus provides a speaking position in culture/within the symbolic order
a: relating to the signifying nature of the phallus
b: our sexual identity informed through the phallus
Words only mean things in differentiation to other words. Presence, having, not having
The role of the symbolic phallus
The 'orders' of reality
The real:
- that which cannot be symbolised/signified
-where our most basic,animal selves exist
The imaginary:
- the order which exists before symbols and significations
Ego is born and develops
No discions between self and other/subject and object
The symbolic:
-'the order of the Other'
- exists outside ourselves - language exists before and outside of us
- the order that allows us to exist within a culture of others
Psychoanalysis and art criticism/theory
Human subjectivity - what it is to be human, motivation, desires the unconscious
- to help us understand why things are as they are
David Lynch constantly references psychoanalysis. The first 2/3's of the film are about hidden desire.
Model-based theory/paradigm - Models provide a tool for categorising or breaking down individuals and groups of art/design works
EDWARD BERNAYS
- The Godfather of PR. Freud's nephew
Applied knowledge of psychoanalysis, unconscious desire to advertising and PR campaigns
SELLING DESIRES, LIFESTYLES, NEEDS AND WANTS
Revolutionised advertising by applying manipulation techniques
Check out Edward Bernays
Sketchy characters, entire Freud family. Basically psychoanalysis was founded by people that didn't like people. Didnt think people could be happy, could be free-thinkers etc. Same with Freud and Bernays
Case Study - 'Torches of Freedom'
Embedding desire within products. Such as cigs ^^^
Max Ernst - Collages c1930
Surrealist. Allowed collage to manipulate the work. Allowed the objects the forms to inform the collage itself, therefore providing this automatic, unconscious element.
Victor Burgin - The Bridge - 1984
Hitchcock's Vertigo
Louise Bourgeois - Spiral Woman - 1952







No comments:
Post a Comment